Epidemiology
Nonfatal Maltreatment of Infants — United States, October 2005–September 2006
Summary: 23.2 children per 1,000 population aged <1 year experienced substantiated nonfatal maltreatment in the United States.
Tobacco exposed infants
Tobacco smoke is widely believed to be the most common and dangerous of the environmental toxins to which children are exposed. It is connected with a wide range of childhood conditions such as respiratory tract infections, asthma, otitis media (middle ear infection) and sudden infant death syndrome.
- The Burden of Environmental Tobacco Smoke Exposure on the Respiratory Health of Children 2 Months Through 5 Years of Age in the United States: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988 to 1994 Peter J. Gergen, Jean A. Fowler, Kurt R. Maurer, William W. Davis, and Mary D. Overpeck, PEDIATRICS Vol. 101 No. 2 February 1998
- Prenatal and Postnatal Environmental Tobacco Smoke Exposure and Children’s Health. Joseph R. DiFranza, C. Andrew Aligne and Michael Weitzman. PEDIATRICS Vol. 113 No. 4 April 2004, pp. 1007-101
- Maternal Smoking and Infantile Gastrointestinal Dysregulation: The Case of Colic. Shenassa, Edmond and Brown, Mary-Jean. Pediatrics; Oct2004, Vol. 114 Issue 4, p497, 9p [Full text available on EBSCO Host: Accession Number: 14488773]
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) and
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)
Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can impede fetal growth. It can also lead to congenital anomalies and to mental retardation. In several states infants born with this syndrome must be reported to protective services. FASD is the largest preventable cause of mental retardation and birth defects. FASD affects 1 in 100 live births or as many as 40,000 infants each year in the US.
Here are the rather grim statistics on binge drinking in the US among pregnant women (NP means “not pregnant”). Eight percent of pregnant women binge drink during the first trimester! Almost twenty percent of toddler’s moms binge drink.
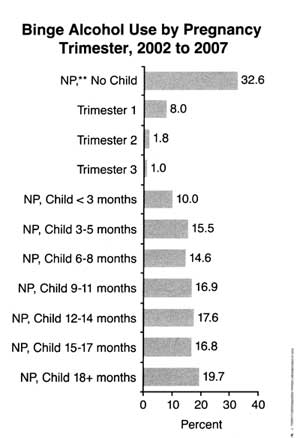
Source: SAMHSA, Office of Applied Studies (May 21, 2009). The NSDUH Report: Substance Use among Women During Pregnancy and Following Childbirth. Full report available here.
Death by Meth
Death by methamphetamine toxicity of breast milk
“Crack Babies”
Effect of prenatal cocaine use on physical growth and development appears to be less detrimental than was once thought. It now seems probable that it’s impact is less than that of tobacco or alcohol exposure. Cocaine exposure does not appear to cause birth defects, does not increase the risk of SIDS, and may not have any effect on IQ of children.
- For a recent overview see: Cocaine: Effects of In Utero Exposure on the Fetus and Neonate. Askin, Debbie Fraser and Diehl-Jones, Bill. Journal of Perinatal & Neonatal Nursing; Mar2001, Vol. 14 Issue 4, p83 [Full text available on EBSCO Host: Accession Number: 6967827]
- For details: Frank DA, Augustyn M, Knight WG, et al.: Growth, development, and behavior in early childhood following prenatal cocaine exposure: A systematic review. Journal of the American Medical Association 2001; 285:1613-1625
[Full text available on EBSCO Host: Accession Number: 4829595] - Hallam Hurt, MD; Elsa Malmud, PhD; Laura Betancourt; Leonard E. Braitman, PhD; Nancy L. Brodsky, Phd; Joan Giannetta, “Children with In Utero Cocaine Exposure Do Not Differ from Control Subjects on Intelligence Testing,” Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, Vol. 151: 1237-1241 (American Medical Association, 1997).
- Bauchner, H., Zuckerman, B., McClain, M., Frank, D., Fried, L.E., & Kayne, H., “Risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome among Infants with In Utero Exposure to Cocaine,” Journal of Pediatrics, 113: 831-834 (1988).
- Martin, M.L., Khoury, M.J., Cordero, J.F. & Waters, G.D., “Trends in Rates of Multiple Vascular Disruption Defects, Atlanta, 1968-1989: Is There Evidence of a Cocaine Teratogenic Epidemic?” Teratology, 45: 647-653 (1992).
Shaken Baby Syndrome
Shaken Baby Syndrome (SBS) results from the violent shaking of an infant or small child. Roughly 25-30% of victims who show up in the medical system die as a result of their injuries. It is probably very underreported both because victims do not always display visible evidence of physical trauma and because it may be difficult for health care providers to distinguish Shaken Baby Syndrome from other forms of physical trauma (falling out of bed etc.).
- National Center on Shaken Baby Syndrome
- Shaken baby syndrome—an introduction to the literature. Philip Wheeler, Child Abuse Review; Nov/Dec2003, Vol. 12 Issue 6, p401, 15p [Full text available on EBSCO Host: Accession Number: 12215714]
Munchausen Syndrome by Proxy / Factitious Disorder
Munchausen Syndrome by Proxy is a pattern of behavior in which caretakers deliberately exaggerate and/or fabricate and/or induce physical and/or psychological-behavioral-mental health problems in others. Most common in parents of infants or toddlers.
Postpartum Mood Disorders
Ten to 20 percent of new mothers develop a full-blown clinical depression, which can last from two weeks to as long as a year. Depression is a signifcant risk factor for childhood neglect.
Gender specific child abortion and/or infanticide
- Elizabeth Gerhardt, The Cross and Gendercide: A Theological Response to Global Violence Against Women and Girls (InterVarsity Press, 2014)
- Jha, Prabhat, et al. Low male-to-female sex ratio of children born in India: national survey of 1.1 million households. Lancet; 1/21/2006, Vol. 367 Issue 9506, p211-218 [Full text available on EBSCO Host: Accession Number: 19472209 ]
- Barbara D. Miller The Endangered Sex: Neglect of Female Children in Rural North India (Oxford University Press, 1997) ISBN: 0195641558
- Marvin Kohl, ed., Infanticide and the Value of Life (Prometheus Books, 1978) ISBN: 0879751002
Boarder Babies, Abandoned Infants and Discarded Infants
Boarder babies are infants under the age of 12 months who remain in the hospital past the date of medical discharge. Boarder babies may eventually be claimed by their parents and/or be placed in alternative care. Abandoned infants are newborn children who are not medically cleared for hospital discharge, but who are unlikely to leave the hospital in the custody of their biological parents. Discarded infants are newborns who have been abandoned in public places, other than hospitals, without care or supervision.
Homelessness and Neglect of Infants
One quarter of the homeless population in the US are families with very young children. Infants without proper shelter are obviously at high risk for physical neglect. Interesting culpability questions arise. Is it the parents who are responsible? A culture that tolerates homelessness? Bottom line: trying to understand abuse outside of it’s social context is probably a serious mistake.
Abortion
At both ends of the life cycle (abortion and euthanasia) you find highly contentious issues of many kinds. The language of abuse (abuser, perpetrator, etc) tends to become highly politicized in these contexts. For some people, removing a blastocyst from a uterus is a form of child murder. Others argue that forcing an adolescent to carry to term an unwanted pregnancy resulting from rape is a form of child abuse. I do not intend to explore these contentious issues in this context. It would be worth a few moments, however, to reflect on why there is enormous public interest at the extremes of the life cycle but a comparatively lower level of interest in abuse during other life stages.
Medical Treatment of Infants with Multiple Congenital Abnormalities (“Baby Doe” cases)
The extent to which aggressive medical intervention is appropriate with newborn infants with multiple congenital abnormalities is a matter of considerable contention. In particular, the extent to which ‘quality of life’ assessments ought to play a role in such decisions is highly contentions — some seeing any such role to be a kind of abuse by medical neglect. Legislation passed in the 1980’s (Federal Child Abuse and Neglect Act) sought to provide some guidance for these matters but in all probability such difficult and complicated decisions will continue to remain difficult and complicated.
